reading-notes
Reading Notes for Codefellows!
Project maintained by AlanYHung Hosted on GitHub Pages — Theme by mattgraham
Code 401 ASP.NET
Reading 05
(All My Notes are attributed/sourced from the Resources directly preceding them.)
Linked Lists
Author: CodeFellows
- Linked Lists are data structures that contain the properties of values and one or more pointers
- Pointers are variables the reference the address of connected nodes.
- Generally pointers will point to the next node or previous nodes.
- When traversing a Linked List you always have to start at the beginning and go through each connected Node.
- Big O efficiency is usually O(n) and/or O(1)
What’s a Linked List, Anyway? [Part 1]
Author: Vaidehi Joshi
- Linked Lists are linear data structures meaning you have to traverse every node to get to the value you want to access or add in most cases.
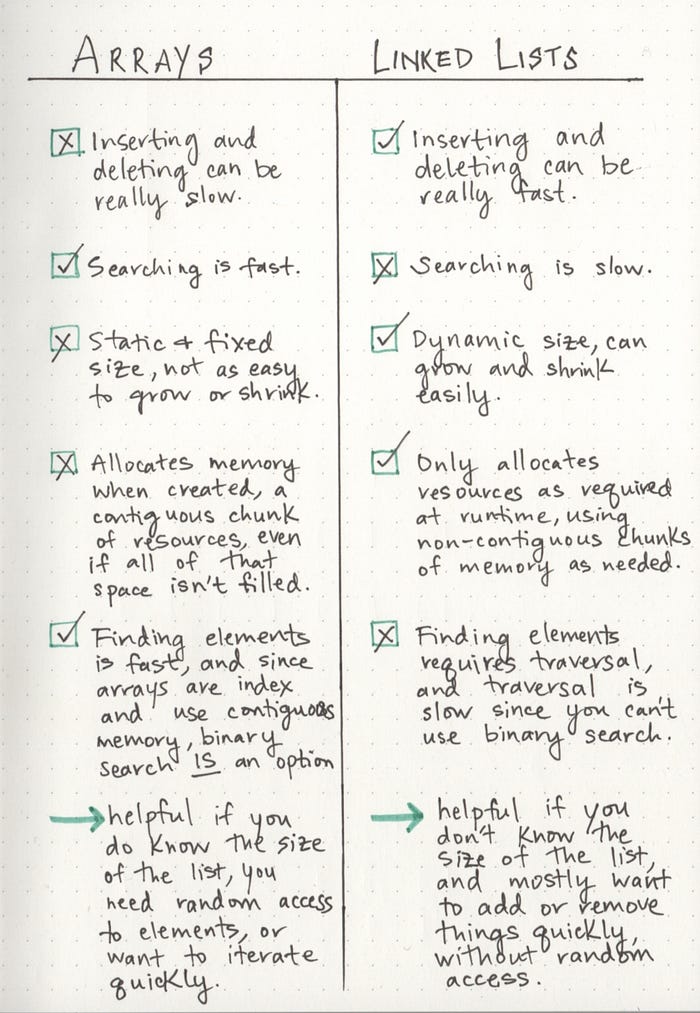
- The difference between Linked Lists and arrays is the way it handles memory.
- Linked Lists can be stored anywhere in memory as they will always point to the next and/or previous node in their list.
- Arrays require a block of contiguous memory of the size required to be available in memory.
What’s a Linked List, Anyway? [Part 2]
Author: Vaidehi Joshi
- Adding new items to the list is simple with linked lists because there is no need to pre-allocate memory.
- Once a new item is added to the list, you just need to rearrange the pointers
- The advantage of linked lists is the dynamic memory management and the speed at which you can add or remove elements.
- The disadvantage of linkedlists is that it is slow to search for a specific item in the list.
- Following is a list of pros and cons between Linked Lists and Arrays.